Tcache attack
工作原理
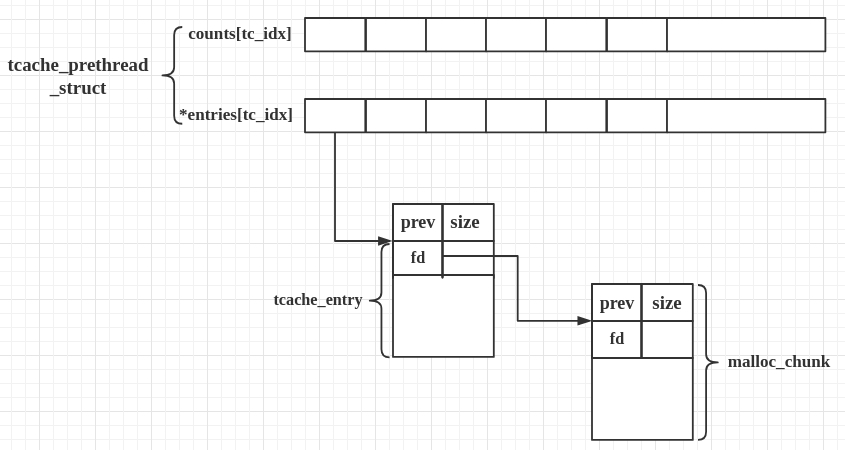
在libc启用tcache后,free后满足一定size的chunk会优先插入tcache。如下图,每个index下是一个单向链表。每个链表最大长度为7个,满了后进入fastbin或unsortedbin。malloc时,如果满足size,会优先从tcache中取回,若tcache中已空则查看fastbin、smallbin或unsortedbin。
Tcache perthread corruption
tcache的metadata位于heap段首,其定义如下:
typedef struct tcache_entry
{
struct tcache_entry *next;
} tcache_entry;
typedef struct tcache_perthread_struct
{
char counts[TCACHE_MAX_BINS];
tcache_entry *entries[TCACHE_MAX_BINS];
} tcache_perthread_struct;
# define TCACHE_MAX_BINS 64
对应于上述的数据结构,首先是一个是0x40字节的counts数组,接着是tcache_entry的指针数组,大小为0x40 * 8,每个成员为每个tcache链表的头指针。
整个tcache metadata部分也可视为一个chunk,再加上最开始的chunk header(size of chunk = 0x251),其总大小为0x10 + 0x40 + 0x40 * 8 = 0x250。
通过篡改这个tcache header,我们可以操纵tcache中存储的内容,如链表的FD指针指向伪造的chunk,以及count值等。
Tcache dup
通过double free漏洞,两次free使同一个chunk被加入tcache两次。重新malloc第一次后,取回该chunk,得以改写其FD指针;第二次malloc后,就可以取到被篡改的FD指针所指向的伪chunk。
libc leak
free同一个size的不同chunk超过7个后,第8个进入unsortedbin。此时unsortedbin的chunk的内容为一个libc地址。